What is a chocolate machine?
Chocolate machine is a device used to melt, mix, and shape chocolate into various shapes and sizes. It can be used to make various chocolates, such as truffles, chocolate bars, and cupcakes.
A chocolate machine usually consists of two basic components – a melting and tempering unit and a forming unit. The melting and tempering device can be powered by electricity or natural gas to achieve the appropriate temperature and texture of chocolate. The forming unit consists of a frame with interchangeable molds and other accessories that can be used to shape chocolate into various shapes.
For anyone interested in making chocolate, a chocolate machine is a great tool. With the right equipment and knowledge, homemade chocolate can be quickly and easily made.
History of Chocolate Machine Development
The development history of chocolate machines is a process spanning several centuries, and significant progress has been made in the production, processing, and consumption of chocolate.
In the 18th century, chocolate presses were developed to extract cocoa butter from roasted cocoa beans and produce cocoa solids that could be used to make cocoa powder. This innovation marks an important step towards separating cocoa butter from cocoa blocks.
In 1879, Swiss chocolate manufacturer Rudolf Lind invented the Conch Machine, a revolutionary development that changed the texture and taste of chocolate. The conch process includes long-term continuous mixing and aerated chocolate, making the chocolate smoother and more refined, and improving the flavor and taste.
At the end of the 19th century, machines that could shape chocolate into various shapes emerged, leading to the large-scale production of chocolate bars and other shaped chocolate products. This makes the shape and size more consistent.
Throughout the 20th century, continuous refining and tempering machines were developed. The refining machine further processes chocolate blocks to obtain a smooth texture, while the tempering machine ensures that the chocolate has the required crystal structure to achieve a glossy appearance and taste.
With the development of the chocolate industry, automatic packaging machines have been introduced, enabling efficient packaging of chocolate bars and other products. These machines have greatly increased production capacity.
In the second half of the 20th century, computer control and automation became a part of the development of chocolate machines. CNC technology (computer numerical control) allows for precise control of various aspects of chocolate production, including molding, wrapping (chocolate coating), and decoration.
Further innovation has emerged in the development of chocolate machines in the 21st century. 3D printing technology has been applied to chocolate, enabling chocolate manufacturers and candy manufacturers to create complex customized chocolate sculptures. In addition, the advancement of robots and artificial intelligence can help improve the efficiency and accuracy of the chocolate production process.
In recent years, the development of chocolate machines has increasingly focused on sustainability. Manufacturers are exploring energy-saving solutions, reducing waste, and environmentally friendly materials to minimize the ecological impact of chocolate production.

Main application fields of chocolate machine
Chocolate machines are widely used in various industries, each contributing to different stages of chocolate production and preparation.
Chocolate production: The chocolate machine plays a central role in the process of producing chocolate from cocoa beans. They are used for baking, crushing, screening (removing the shell), and grinding cocoa beans into cocoa balls or liquid. The thickener refines and inflates chocolate, while the lighter ensures a suitable crystal structure to obtain a smooth surface and bite.
Forming and Enrobing: Chocolate molding machines are used to produce chocolate bars, candies, and other shaped chocolate products. These machines can produce products of various shapes and sizes with consistent accuracy. The Enrobing machine applies a thin layer of chocolate to products such as cookies or fruits, making the surface smooth and even.
Decorate and customize chocolate: A 3D printer suitable for chocolate can create complex and personalized chocolate sculptures and decorations. These machines are used to create customized gifts, event centers, and art chocolate displays.
Packaging and Packaging: Automatic packaging machines are used for efficient packaging of various forms of chocolate products, including individual bars, classifications, and boxes. These machines ensure hygiene, consistency, and efficiency during the packaging process.
Candy industry: In addition to traditional chocolate, these machines are also used to produce various candies, such as coated nuts, candies, truffles, and gummies. Enrobing machines are often used to coat chocolate on various candy centers.
Baking and pastry: Chocolate machines are used in the baking and pastry industry to make chocolate decorations, fillings, and coatings for pastries, cakes, and desserts. Enrobing machine can be used to apply chocolate or other coatings on baked goods.
Food Services and Hotels: In the food services industry, coffee shops, restaurants, and hotels all use chocolate machines to make hot chocolate, chocolate sauce, and chocolate desserts. A machine that can melt and maintain chocolate at a specific temperature is crucial for maintaining quality.
Educational use: The chocolate machine is used in cooking schools and training centers to teach students the process of making chocolate, including baking, refining, tempering, and shaping.
Home use: A small chocolate machine can be used by family enthusiasts who want to try making their own chocolate products, such as truffles, chocolate bars, and decorations.
What is the classifications of chocolate machine?
Chocolate processing machine:
Baking machine: used for baking cocoa beans, developing flavor and aroma.
Cracking and Winning Machine: Separating cocoa kernels from fruit shells.
Grinder: Grinds cocoa granules into cocoa blocks or cocoa liquid.
Thickener: Refines and inflates chocolate to improve texture and flavor.
Reflexer: Control the crystal structure of chocolate to make it shiny and brittle.
Forming machine:
Chocolate Forming Machine: Produces various shapes and sizes of chocolate bars and products.
Enrobing Machines: Apply a layer of chocolate to the product to make the surface smooth.
Depositor: Accurately deposit fillers into chocolate molds or shells.
Truffle rolling machine: Use cocoa powder or other coatings to shape and apply truffles.
Packaging machine:
Packaging machine: Automatically packaging individual chocolate bars or products.
Packaging machine: Packaging chocolate products into boxes, various products, or bags.
Sealing machine: Seal the packaging to maintain freshness and prevent contamination.
Decoration and customization machines:
3D printer: Produce complex and customized chocolate sculptures and decorations.
Chocolate spray machine: Apply a thin layer of chocolate for decoration.
Chocolate transfer machine: Transfer complex designs to the surface of chocolate.
Laboratory and R&D Machines:
Small refining and thickening machine: used for the research and development of chocolate formulas.
Texture analyzer: measures and analyzes the texture and consistency of chocolate samples.
Hot chocolate machine:
Commercial hot chocolate dispenser: Prepare and distribute hot chocolate in a food service environment.
Household Hot Chocolate Maker: A device for making hot chocolate at home.
Nut and ingredient dispenser:
Nut dispenser: Accurately distribute nuts and other contents onto chocolate products.
Sprinkler: Sprinkle sprinklers and sprinklers onto chocolate coated items.
Industrial and large machinery:
Mass production line: A comprehensive system for large-scale chocolate production.
Automated packaging production line: Integrating multiple machines to achieve efficient packaging of chocolate products.
Handmade and handmade chocolate machines:
Small batch refining machine: Used by craft chocolate manufacturers to refine small amounts of cocoa.
Hand dipping tool: Assist craftsmen in manually dipping chocolate.
Candy Machinery:
Candy coating machine: uses chocolate to coat various centers, such as nuts or candy.
Fructose filling machine: Inject filling into chocolate shells to make fructose.
Food processing machinery:
Baking and pastry machines: Make chocolate decorations, coatings, and fillings for baked goods.
Ice cream and frozen dessert equipment: Add chocolate to the frozen dessert.
Maintenance content of chocolate machine
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the lifespan, efficiency, and safety of the chocolate machine. Regular maintenance helps prevent malfunctions, minimize downtime, and maintain the quality of chocolate production.
Clean all accessible parts of the machine, including surfaces, hoppers, chutes, and conveyors.
Remove remaining chocolate and debris to prevent contamination and blockage.
Check and clean the cooling system to maintain appropriate temperature control.
Lubricate the moving parts according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Check the belts, chains, and other drive components for wear and tension.
Ensure that the moving parts are correctly aligned.
Arrange qualified technical personnel to conduct professional inspections every year.
Friendly reminder:
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance plan and guidelines.
Record the maintenance tasks performed and any issues encountered.
Train employees on correct machine operation, maintenance, and safety regulations.
Use recommended cleaning agents and lubricants to avoid damage.
Prepare spare parts for quick replacement.
Timely handle any abnormal noise, vibration, or changes in machine behavior.
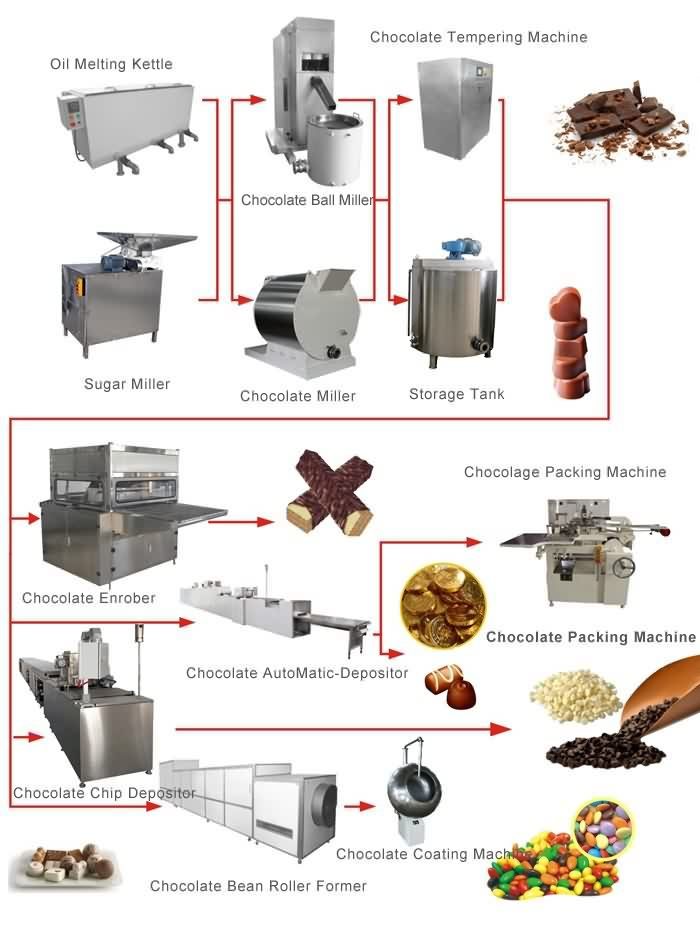
Detailed explanation of chocolate machine production process
The production process of a chocolate machine includes several stages, converting raw cocoa beans into the final chocolate product. This process includes various steps from bean processing to molding and packaging.
Cocoa bean processing:
Cleaning and classification: Clean raw cocoa beans to remove any debris, stones, or foreign objects. Then classify them to ensure that only high-quality beans are used.
Baking: Bake cleaned beans to create flavor and aroma. Baking also helps reduce moisture content and sterilize beans.
Bursting and Winning: Burst the roasted beans and separate the shell (shell) from the fruit grains. Winning then removes the fruit shell, leaving behind the cocoa seeds.
Cocoa paste grinding and refining:
Grinding: Cocoa granules are ground into a paste, called cocoa blocks or cocoa liquid. The grinding process generates heat, causing the cocoa solids to liquefy.
Refining: Cocoa blocks are further refined in a conch machine. Concentration involves continuous mixing and grinding, enhancing the texture and flavor of chocolate by reducing particle size and developing smoothness.
Tempering and mixing:
Tempering: Tempering refined chocolate to ensure it has an appropriate crystal structure, resulting in a shiny and fractured surface. This includes controlling heating, cooling, and stirring.
Chocolate mixing: Depending on the desired product, additional ingredients such as milk powder, sugar, emulsifiers, and seasoning can be added and mixed into tempered chocolate.
Forming and Enrobing:
Forming: Pour tempered chocolate into a mold to determine the shape and size of a chocolate bar or product. Vibration can be used to remove bubbles and ensure uniform distribution.
Cooling and solidification: The filled mold is cooled to solidify the chocolate. This ensures that the chocolate maintains its desired shape and texture.
Demolding: After the chocolate has completely solidified, open the mold and remove the chocolate product.
Packaging: For products that require chocolate coating, the packaging process involves applying a layer of tempered chocolate to items such as cookies, nuts, or fruits.
Cooling and Candy Forming:
Cooling channel: Chocolate products are cooled in the cooling channel to stabilize their structure and prevent flowering (white stripes caused by fat migration to the surface).
Filling and molding: Some chocolate machines can put the filling material into the mold before the chocolate shell is formed. This leads to products like filled chocolate or fructose.
Packaging and quality control:
Packaging: Chocolate products are packaged using automatic packaging machines, boxes, or other packaging methods after cooling and solidification.
Quality control: Inspect chocolate products for defects, inconsistencies, and quality issues throughout the entire production process. This may include visual inspection, weight inspection, and flavor and texture testing.
Storage and Delivery:
Storage: Packaged chocolate products are stored under appropriate conditions to maintain freshness and quality, including temperature and humidity control.
Distribution: The distribution of finished chocolate products to retail stores, wholesalers, or directly to consumers.